In C programming, a data type is a set of values and is set to work on those values. C provides different types of data types that allow the programmer to select the appropriate type of variable so that its value can be determined.Each variable of C has an associated data type. Different data types require different amount of storage and there are specific operations that can be done on it.
In a programming language, there is a collection of data-type data that has specific meanings as well as attributes. Some of them are an integer, floating point, character, etc. Typically, programming languages specify category values for the given data-type.
C data types are used to :
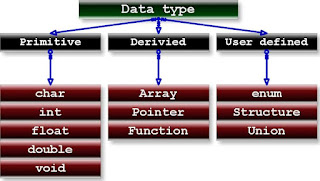
Primitive Data Types
User defined Data Types
Structure:-It is a package of different types of variables under one name. This is done efficiently to handle the data. The keyword "struct" is used to define a structure.
Union:- allow different data types to be stored in the same storage location. Programmers can define a union with different members, but only one member can have one value at a given time.
Enum:-Enumeration is a special data type that has integral constants, and each of them is assigned with a specific name. The keyword "enum" is used to define enumerated data types.
In a programming language, there is a collection of data-type data that has specific meanings as well as attributes. Some of them are an integer, floating point, character, etc. Typically, programming languages specify category values for the given data-type.
C data types are used to :
- When it is declared, then identify the type of a variable.
- Identify the type of return value of a function.
- Identify the type of parameter desired by a function.
- Primitive DT :- int,float,char,void
- Derived DT :- Array,Pointer,Function
- User Defined DT :- enum,structure, union
Primitive Data Types
- char: The most basic data type in C. It stores a single character and requires a single byte of memory.
- int: an int variable is used to store an integer.
- float: It is used to store decimal numbers (numbers with floating point value).
- double: It is used to store decimal numbers (numbers with floating point value) with double precision.
Different data types also have different ranges upto which they can store numbers.we show this ranges
With format specifiers..
| Data Type | Memory (bytes) | Range | Format Specifier |
|---|---|---|---|
| short int | 2 | -32,768 to 32,767 | %hd |
| unsigned short int | 2 | 0 to 65,535 | %hu |
| unsigned int | 4 | 0 to 4,294,967,295 | %u |
| int | 4 | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 | %d |
| long int | 4 | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 | %ld |
| unsigned long int | 4 | 0 to 4,294,967,295 | %lu |
| long long int | 8 | -(2^63) to (2^63)-1 | %lld |
| unsigned long long int | 8 | 0 to 18,446,744,073,709,551,615 | %llu |
| signed char | 1 | -128 to 127 | %c |
| unsigned char | 1 | 0 to 255 | %c |
| float | 4 | %f | |
| double | 8 | %lf | |
| long double | 12 | %Lf |
Declaration of primitive Data Types with variables :-
int age;
char letter;
float height, width;
Derived Data Types
Array:- Arrays are sequences of data items having homogeneous values. They have adjacent memory locations to store values.
Pointer:- These are powerful C features which are used to access the memory and deal with their addresses.
User defined Data Types
Structure:-It is a package of different types of variables under one name. This is done efficiently to handle the data. The keyword "struct" is used to define a structure.
Union:- allow different data types to be stored in the same storage location. Programmers can define a union with different members, but only one member can have one value at a given time.
Enum:-Enumeration is a special data type that has integral constants, and each of them is assigned with a specific name. The keyword "enum" is used to define enumerated data types.













No comments:
Post a Comment