Break, Continue and Goto Statement in C++ | C++ break,continue, goto statement | C++ conditional statements | My CS Tutorial
Control Statement and Description
break statement - Terminates the loop or switch statement and
transfers execution to the statement immediately following the loop or switch.
continue statement - Causes the loop to skip the remainder of its body and immediately retest its condition prior to reiterating.
goto statement - Transfers control to the labeled statement.
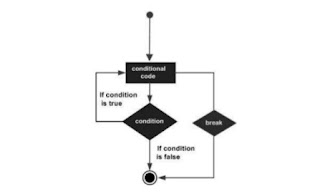
break Statement
The break statement in C programming has the following two usages:
When a break statement is encountered inside a loop, the loop is immediately terminated and the program control resumes at the next statement following the loop.
It can be used to terminate a case in the switch statement (covered in
the next chapter).
If you are using nested loops, the break statement will stop the execution of the innermost loop and start executing the next line of code after the block.
Syntax
The syntax for a break statement in C++ is as follows:
break;
Flow Diagram
Example
#include <iostream.h>
int main ()
{
/* local variable definition */
int a = 10;
/* while loop execution */
while( a < 20 )
{
cout<<"value of a: %d\n"<<a;
a++;
if( a > 15)
{
/* terminate the loop using break statement */
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result:
value of a: 10
value of a: 11
value of a: 12
value of a: 13
value of a: 14
value of a: 15
continue statement
The continue statement in C++ programming works somewhat like the break statement. Instead of forcing termination, it forces the next iteration of the loop
to take place, skipping any code in between.
For the for loop, continue statement causes the conditional test and increment portions of the loop to execute. For the while and do...while loops, continue statement causes the program control to pass to the conditional tests.
Syntax
The syntax for a continue statement in C is as follows:
continue;
Flow Diagram
Example
#include <iostream.h>
int main ()
{
/* local variable definition */
int a = 10;
/* do loop execution */
do
{
if( a == 15)
{
/* skip the iteration */
a = a + 1;
continue;
}
cout<<"value of a: %d\n"<<a;
a++;
}while( a < 20 );
return 0;
}
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result:
value of a: 10
value of a: 11
value of a: 12
value of a: 13
value of a: 14
value of a: 16
value of a: 17
value of a: 18
value of a: 19
goto statement
A goto statement in C++ programming provides an unconditional jump from the ‘goto’ to a labeled statement in the same function.
NOTE: Use of goto statement is highly discouraged in any programming language because it makes difficult to trace the control flow of a program, making the program hard to understand and hard to modify. Any program that
uses a goto can be rewritten to avoid them.
Syntax
The syntax for a goto statement in C is as follows:
goto label;
..
.
label: statement;
Here label can be any plain text except C/C++ keyword and it can be set anywhere in the C++ program above or below to goto statement.
Flow Diagram
Example
#include <iostream.h>
int main ()
{
/* local variable definition */
int a = 10;
/* do loop execution */
LOOP:do
{
if( a == 15)
{
/* skip the iteration */
a = a + 1;
goto LOOP;
}
cout<<"value of a: %d\n"<<a;
a++;
}while( a < 20 );
return 0;
}
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result:
value of a: 10
value of a: 11
value of a: 12
value of a: 13
value of a: 14
value of a: 16
value of a: 17
value of a: 18
value of a: 19
The exit function
exit is a function defined in the cstdlib library.
The purpose of exit is to terminate the current program with a specific exit code. Its prototype is:-
void exit (int exitcode);
The exitcode is used by some operating systems and may be used by calling programs. By convention, an exit code of 0 means that the program finished normally and any other value means that some error or unexpected results happened.
Break, Continue and Goto Statement in C++ | C++ break,continue, goto statement | C++ conditional statements | My CS Tutorial
_______________________________________
Please share this post and blog link with your friends.For more programs use this blog.
If you have any problem, please comment in comment box, subscribe this blog for notifications of new post on your email and follow this blog.If you have any method of this tutorial or program or want to give any suggestion send email on hc78326@gmail.com
Created by-- HARSH CHAUHAN















No comments:
Post a Comment