C - Type Casting | Type casting in c | Implicit, explicit | Type conversions in c | Example | Usual arithmetic conversion | Integer promotion | My CS Tutorial
In programming languages, if the expression contains two or more different datatypes values then they must be converted to the single data type of destination datatype. Here the destination is the location where the final result of that expression is stored.
For example, the multiplication of an integer data value with the float data value and storing the result into a float variable. In this case, the integer value must be converted to float value so that the final result is a float datatype value.
Type casting in C
(type_name) expression
Consider the following example where the cast operator causes the division of
one integer variable by another to be performed as a floating-point operation:-
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
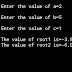
int sum = 27, count = 5;
double mean;
mean = (double) sum / count;
printf("Value of mean : %f\n", mean );
}
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result:-
Value of mean : 5.400000
It should be noted here that the cast operator has precedence over division, so the value of sum is first converted to type double and finally it gets divided by count yielding a double value.
Type conversions
Type conversions can be implicit which is performed by the compiler
automatically, or it can be specified explicitly through the use of the cast
operator. It is considered good programming practice to use the cast operator whenever type conversions are necessary.
Integer Promotion
Integer promotion is the process by which values of integer type "smaller"
than int or unsigned int are converted either to int or unsigned int. Consider
an example of adding a character with an integer:-
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
int i = 17;
char c = 'c'; /* ascii value is 99 */
int sum;
sum = i + c;
printf("Value of sum : %d\n", sum );
}
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result:
Value of sum : 116
Here, the value of sum is 116 because the compiler is doing integer promotion
and converting the value of 'c' to ASCII before performing the actual addition
operation.
Usual Arithmetic Conversion
The usual arithmetic conversions are implicitly performed to cast their values
to a common type. The compiler first performs integer promotion; if the
operands still have different types, then they are converted to the type that
appears highest order. Datatypes converted from low data types to high datatypes like:
int datatype in float datatype
float datatype in double datatype
The usual arithmetic conversions are not performed for the assignment
operators, nor for the logical operators && and ||. Let us take the following
example to understand the concept:-
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
int i = 17;
char c = 'c'; /* ascii value is 99 */
float sum;
sum = i + c;
printf("Value of sum : %f\n", sum );
}
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result:
Value of sum : 116.000000
Here, it is simple to understand that first c gets converted to integer, but as the final value is double, usual arithmetic conversion applies and the compiler converts i and c into ‘float’ and adds them yielding a ‘float’ result.
C - Type Casting | Type casting in c | Implicit, explicit | Type conversions in c | Example | Usual arithmetic conversion | Integer promotion | My CS Tutorial
_______________________________________
Please share this post and blog link with your friends.For more programs use this blog.
If you have any problem, please comment in comment box, subscribe this blog for notifications of new post on your email and follow this blog.If you have any method of this program or want to give any suggestion send email on hc78326@gmail.com
Created by-- HARSH CHAUHAN















No comments:
Post a Comment